Technologies
The following technologies are widely used in the measurement of surface roughness and surface texture. This is not an exhaustive list. If there is a technology that you feel belongs in this list, please email info@emetrology.com.
-
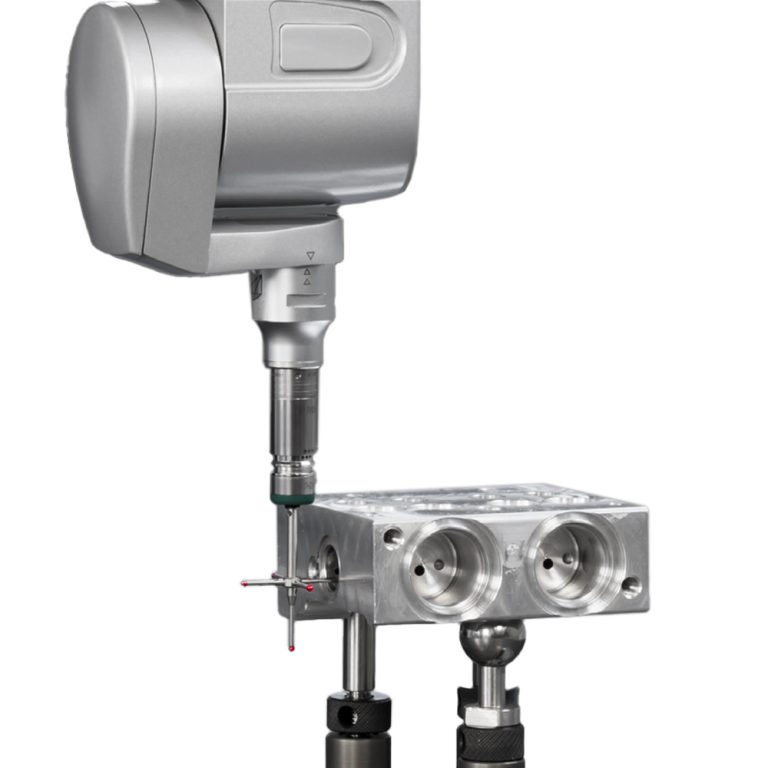

– Coordinate Metrology Basics
Determines the precise 3D geometry of objects using probe- or camera-based systems.
-
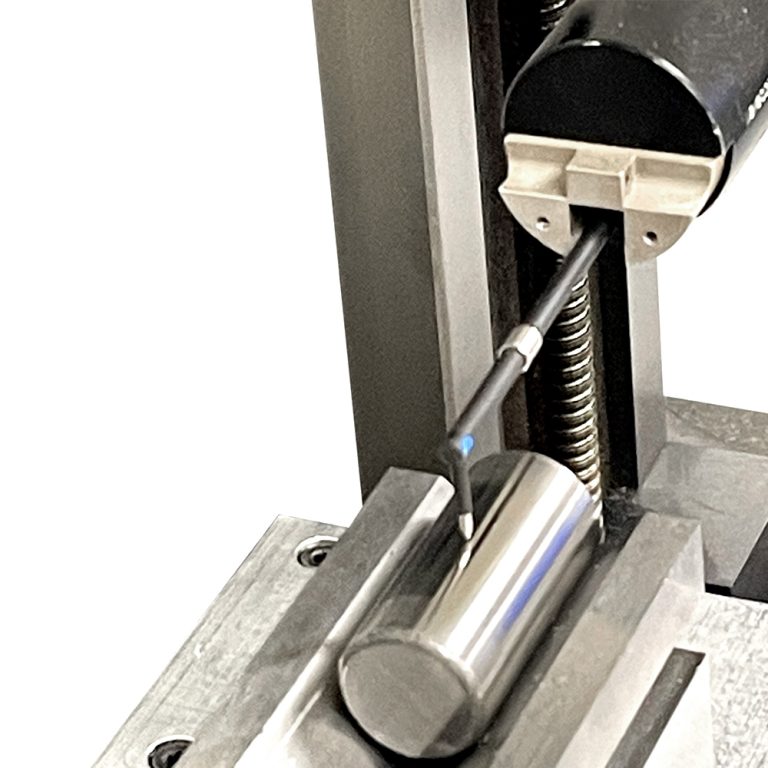

– Form Metrology Basics
Assessment of geometric features such as roundness, flatness, and straightness to ensure part conformance.
-
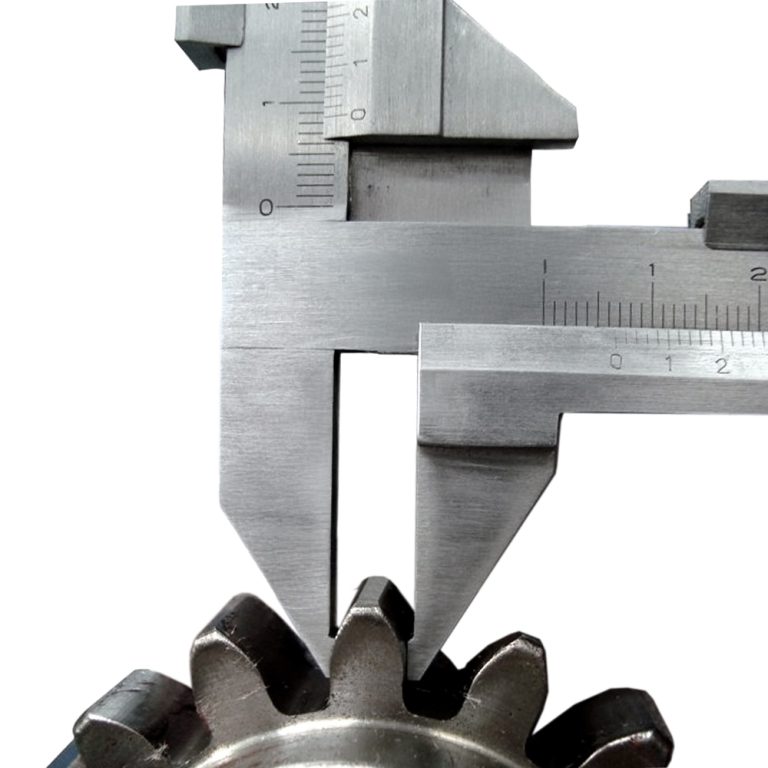

– Gear Metrology Basics
Focuses on verifying gear geometry, performance, and contact conditions.
-
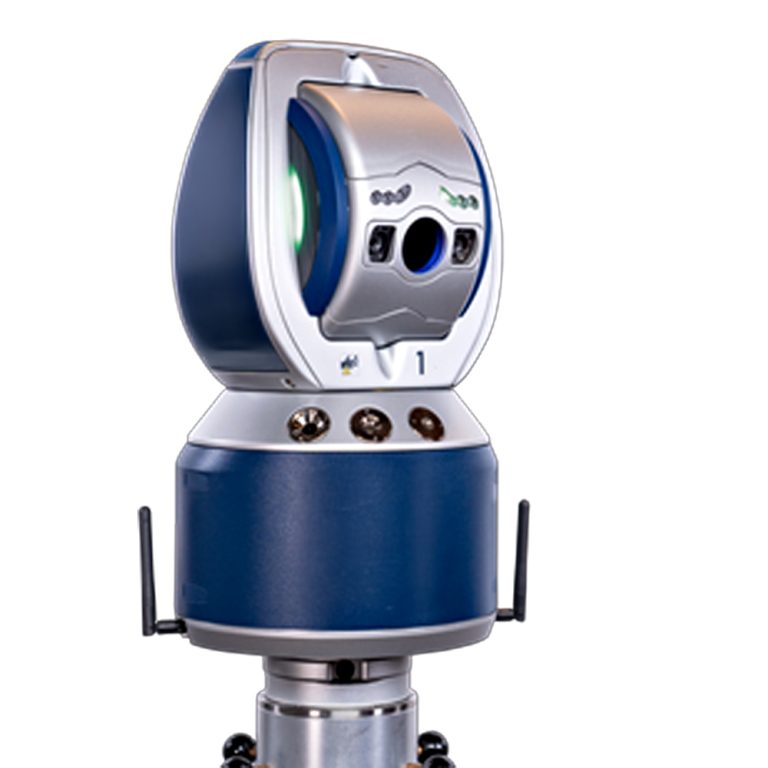

– Large Scale Metrology Basics
Used for inspection of large components or assemblies in aerospace, automotive, or construction.
-

– Length Metrology Basics
Techniques and tools used to measure linear dimensions with high accuracy across various manufacturing environments.
-

– Machine Tool Metrology Basics
Evaluates accuracy and performance of machine tools, crucial for precision manufacturing.
-

– Screw Thread Metrology Basics
Ensures dimensional compliance and functionality of threaded parts.
-

-Surface Metrology Basics
Surface metrology involves measuring surface texture, roughness, and topography using contact or non-contact techniques.
-
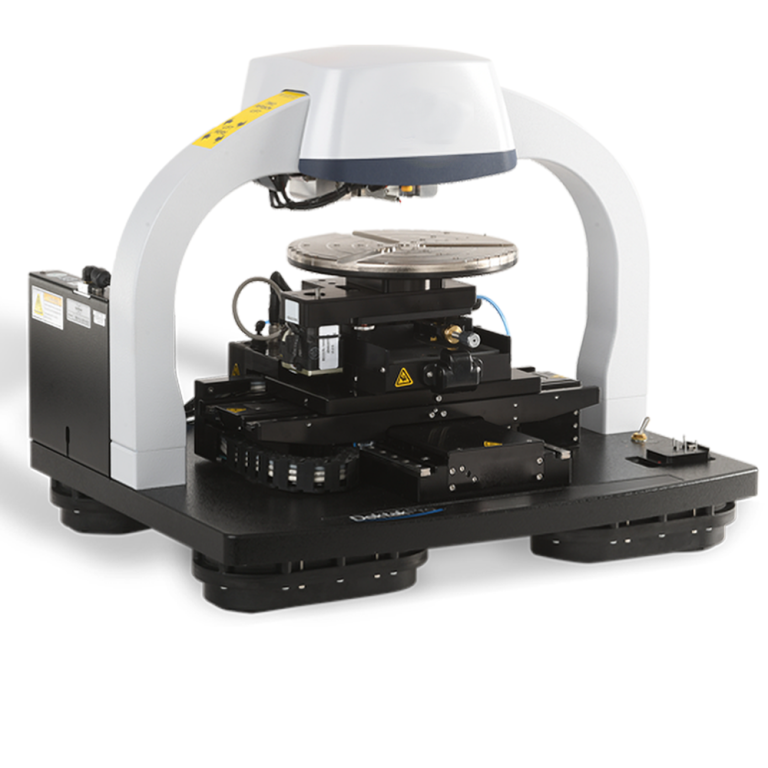

3D Stylus Profiler
A 3D stylus profilometer uses a fine stylus to trace the surface of a part and create a 3D topography map. The stylus moves…
-

Analytical Gear Checking
Analytical gear checking the process of measuring and evaluating the geometry of a gear using parameters to determine how accurately it matches its design…
-
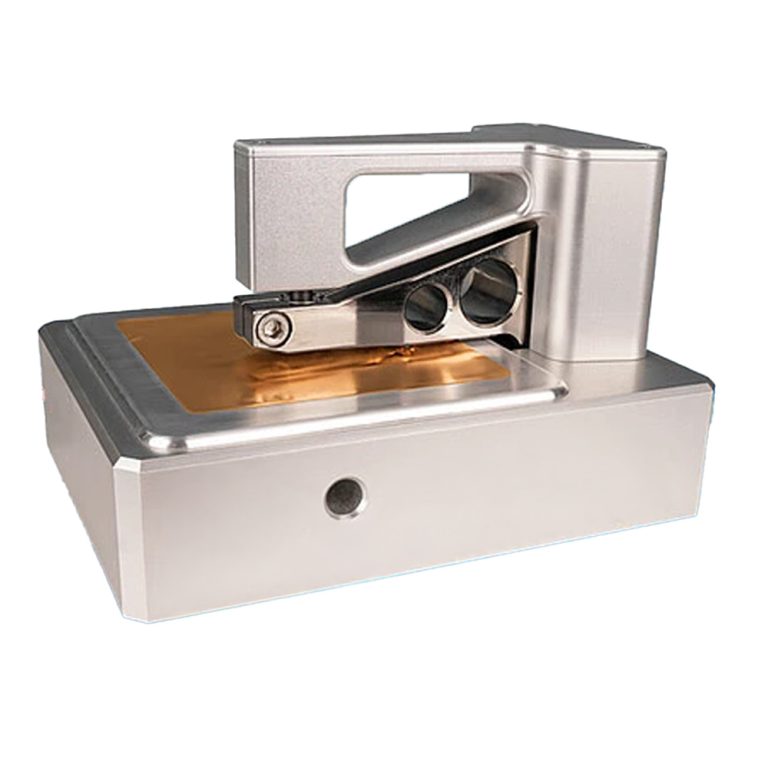

Capacitance Measurement
Capacitance measurement is a non-contact method to assess surface roughness and other characteristics by measuring the capacitance between a probe and the surface. As the…
-
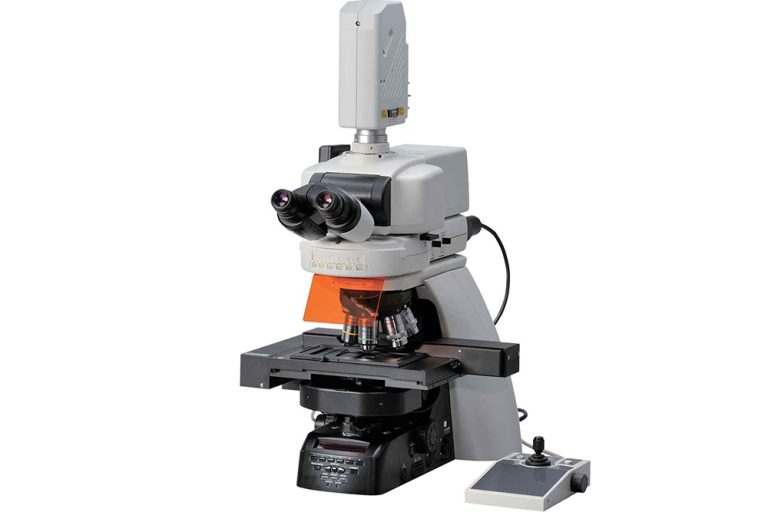

Confocal Microscopy
Confocal microscopy is a technique for measuring surface texture and shape. In a confocal microscope, pinhole aperture is used to create a single focus…
No results found. Not all metrology types have technologies associated with them at this time.
